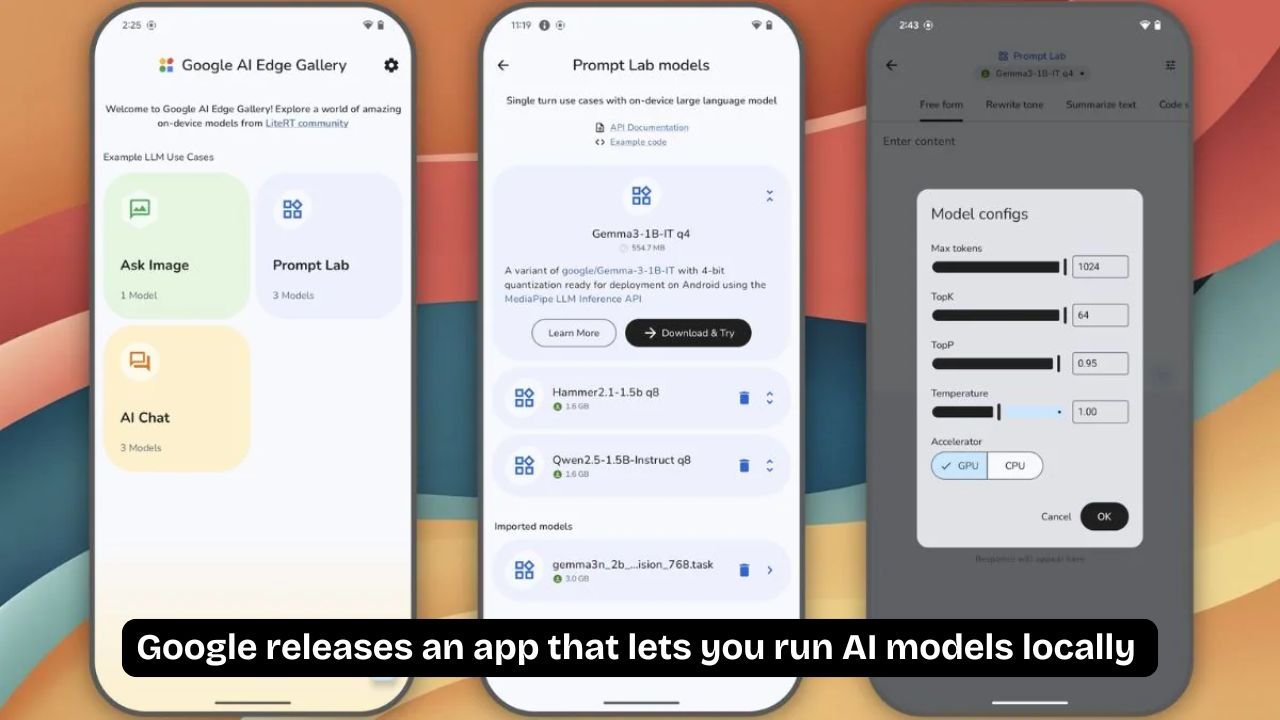
Google has recently launched a groundbreaking app that allows users to run AI models locally on their devices, marking a significant step forward in how artificial intelligence technology can be accessed and utilized. This new app empowers users to harness powerful AI capabilities directly on smartphones, tablets, and other compatible hardware without needing to rely on cloud servers. By enabling local AI model execution, Google is aiming to enhance user privacy, reduce latency, and broaden access to AI-driven features in everyday applications.
Traditionally, many AI-powered applications depend heavily on cloud infrastructure, where data is sent to remote servers, processed, and then returned to the user’s device. While this approach offers access to large-scale computational resources, it raises concerns around data privacy, security, and network dependency. For example, users must have a stable internet connection, and sensitive data sometimes must be transmitted and stored remotely, increasing the risk of unauthorized access or breaches. Google’s new app addresses these issues by bringing the power of AI directly to the device, enabling offline functionality and reducing reliance on external servers.
One of the core advantages of running AI models locally is improved privacy. When AI processing happens on-device, users’ data remains on their own hardware, significantly minimizing exposure to external servers and third parties. This is particularly beneficial for sensitive applications such as personal health monitoring, financial analysis, or confidential communication, where users want to ensure that their information remains private and secure. Google’s approach aligns with growing user demand for privacy-centric technologies, responding to the heightened awareness of digital security risks.
Performance is another key benefit. Running AI locally eliminates the round-trip time involved in sending data to the cloud and waiting for responses, resulting in faster, more responsive interactions. This latency reduction is critical for real-time applications like augmented reality (AR), gaming, and live video processing, where delays can degrade user experience. By enabling local AI computation, Google’s app supports smoother, more immediate functionality, even in environments with poor or no internet connectivity.
The app supports a variety of AI models, from natural language processing and computer vision to speech recognition and predictive analytics. Users can run these models to perform tasks such as image classification, language translation, text summarization, and voice command interpretation, all on-device. This versatility opens up numerous possibilities for developers and end-users alike, allowing more complex AI-driven experiences without the need for constant cloud access.
Google has also focused on making the app developer-friendly. The app includes a user interface and API tools designed to help developers easily integrate local AI models into their own applications. This ecosystem encourages innovation by providing the tools necessary to optimize models for different hardware configurations, ensuring efficient performance across a wide range of devices. Developers can customize and fine-tune AI models to suit their app’s needs, promoting more personalized and relevant AI experiences.
Importantly, Google’s app supports popular open-source AI frameworks such as TensorFlow Lite and ONNX Runtime. By doing so, it leverages the existing AI developer community and enables compatibility with a broad set of pre-trained models and tools. This openness fosters collaboration and accelerates adoption, as developers can reuse and adapt models they are already familiar with for local execution.
The app is designed with scalability in mind, targeting a broad spectrum of devices, from high-end smartphones and tablets to more modest hardware like entry-level devices and IoT gadgets. This inclusivity means AI benefits are not limited to those with premium technology but are accessible to a wider audience. Such democratization of AI aligns with Google’s mission to make technology universally useful and accessible.
One notable use case Google highlights is in healthcare, where running AI models locally can aid in analyzing medical images or monitoring patient data in real time, even in remote locations without reliable internet. By facilitating on-device AI, medical professionals and patients can benefit from faster diagnostics and decision support while maintaining strict data privacy standards.
Google’s app also addresses some of the environmental concerns associated with cloud-based AI processing. Large data centers consume substantial amounts of energy, contributing to carbon emissions and environmental impact. By shifting computation to local devices, the app can reduce the need for energy-intensive server operations and network traffic, potentially lowering the overall carbon footprint of AI applications.
Despite these advantages, running AI models locally presents certain technical challenges. Mobile and edge devices typically have less processing power and memory compared to cloud servers, which limits the size and complexity of models that can be executed effectively. To overcome this, Google’s app employs model optimization techniques such as quantization, pruning, and knowledge distillation to shrink AI models without sacrificing performance. These methods help balance accuracy and efficiency, enabling advanced AI functionality on limited hardware.
Security remains a crucial consideration. While on-device processing enhances privacy by keeping data local, the app must also protect AI models and users’ data from tampering or unauthorized access on the device itself. Google has incorporated security features such as hardware-backed encryption and sandboxing to safeguard the AI environment and maintain data integrity.
Looking ahead, Google plans to continuously expand the app’s capabilities and supported models, incorporating advances in AI research and hardware innovation. The company envisions the app becoming a cornerstone for the next generation of AI-powered applications that are faster, more private, and more versatile.
In conclusion, Google’s new app that enables local execution of AI models represents a significant shift in how AI technology can be delivered and experienced. By prioritizing privacy, responsiveness, and accessibility, the app addresses many limitations of cloud-dependent AI and unlocks new possibilities for developers and users. As local AI computation becomes more feasible and widespread, we can expect to see smarter, more personalized applications that work seamlessly offline and protect user data, heralding a new era of AI integration into everyday life.